Sentences: Definitions, Main Types, and Clear Grammar Examples
Lesson Overview
A sentence is essential for communication, serving different purposes like informing, questioning, or commanding. Sentences can vary in length and complexity, but all convey meaning. Proper structure is crucial to clearly communicate the intended message.
What Is a Sentence?
A sentence is a group of words that expresses a complete thought.
It begins with a capital letter and ends with a punctuation mark, such as a period, question mark, or exclamation mark.
A sentence must have at least one subject (who or what the sentence is about) and one predicate (what the subject does or is).
For example:
The dog runs fast.
In this sentence, "The dog" is the subject, and "runs fast" is the predicate.
Take This Quiz :
Formation of Sentences in English
To build a clear sentence, we need to follow a specific word order. Here's how sentences are typically formed:
- Start with the subject: This is who or what the sentence is about.
- Add the verb: This shows the action or state of being.
- Include the object or other details: This adds more information about the action or subject.
For example: She reads books.
In this sentence, "She" is the subject, "reads" is the verb, and "books" is the object.
Take This Quiz :
Parts of a Sentence
Sentences can be divided into two main parts:
- Subject
The noun, noun phrase, or pronoun that tells us who or what the sentence is about. It typically appears at the start of the sentence.
- Predicate
The part that tells what the subject does or is. It usually begins with a verb and includes all other details in the sentence.
Example:
The teacher explained the lesson clearly.
- Subject: The teacher
- Predicate: Explained the lesson clearly.
Take This Quiz :
Components of a Sentence
A sentence can be made up of five key components:
| Component | Description | Example | Explanation |
| Subject | The person or thing performing the action. | The cat sleeps on the mat. | "The cat" is the subject, performing the action of sleeping. |
| Verb | The action or state of being in the sentence. | The cat sleeps on the mat. | "Sleeps" is the verb, indicating the action the subject is doing. |
| Object | The receiver of the action. | She kicked the ball. | "The ball" is the object, receiving the action of being kicked. |
| Complement | A word/phrase that adds more information about the subject or object. | He is a teacher. | "A teacher" complements the subject "He" by providing more detail. |
| Adjunct | Words or phrases that provide extra details about the action, complement, or other parts of the sentence. | She quickly ran to the store. | "To the store" and "quickly" are adjuncts, providing extra information about the action. |
Note: While most sentences include a subject and a verb, some sentences begin with the verb for emphasis or style.
Types of Sentences
Sentences can be categorized based on their function and structure. There are four types based on function and three based on structure. Let's explore each of them in detail:
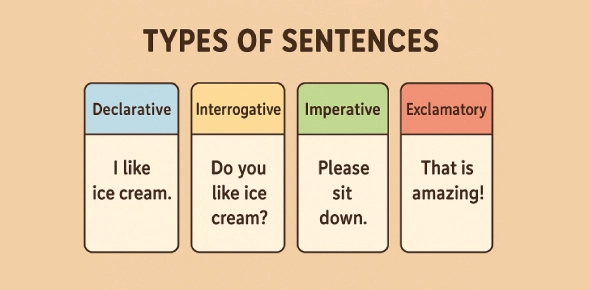
Sentences based on their functions:
| Type of Sentence | Description | Example |
| Declarative Sentence | Makes a statement or provides information. | The sun rises in the east. |
| Imperative Sentence | Gives a command, request, or instruction. Often starts with a verb, no subject. | Close the door quietly. |
| Interrogative Sentence | Asks a question. | What time does the train arrive? |
| Exclamatory Sentence | Expresses strong emotions or excitement. | How amazing that performance was! |
Sentences based on their structure:
| Type of Sentence | Description | Example |
| Simple Sentence | Contains only one independent clause. | The cat jumped onto the table. |
| Compound Sentence | Contains two independent clauses joined by a coordinating conjunction. | She likes to read, and he enjoys playing video games. |
| Complex Sentence | Contains one independent clause and at least one dependent clause. | Because it was raining, we stayed inside. |
| Compound-Complex Sentence | Contains two independent clauses and one or more dependent clauses. | Although it was raining, we went for a walk, and we had a great time. |
Take This Quiz :
Punctuation of Sentences
Punctuation marks depend on the type of sentence. Here are the basic rules:
- Capitalization: The first letter of every sentence must be capitalized.
- Period (.): Used at the end of statements or commands.
- Question Mark (?): Used at the end of questions.
- Exclamation Mark (!): Used to show strong emotions or surprise.
Additionally, commas and semicolons separate clauses in compound and complex sentences. Use commas to list items, and a colon to introduce a list.
Take This Quiz :
Examples of Sentences
- The rainbow stretched across the sky after the rain.
- My cat sleeps on the windowsill, enjoying the sunlight.
- The teacher asked the students to write a poem about nature.
- They walked through the park, enjoying the fresh autumn air.
- The little boy smiled as he saw the puppy wag its tail.
Rate this lesson:
 Back to top
Back to top

.webp)
(89).jpg)