What Is Cellular Respiration Definition, Types, Stages, and Importance? Explore Its Types, Uses & More
Lesson Overview
Cells require energy to function, grow, and repair. This energy comes from food, but it must be converted into a usable form. Cellular respiration is the process that releases this energy, allowing cells to perform essential tasks.
Without cellular respiration, living organisms would not have the energy needed to sustain life. It ensures continuous energy production, making survival possible in diverse environments.
What Is Cellular Respiration?
Cellular respiration is a biochemical process in which cells break down glucose to produce ATP, the primary energy carrier. This process occurs in multiple steps, allowing efficient energy release. Oxygen is required in aerobic respiration, while anaerobic respiration occurs without oxygen, producing less ATP.
The general equation for cellular respiration is:
This process occurs in both plants and animals, ensuring that cells receive a constant supply of energy. It happens at the cellular level, primarily inside the mitochondria, often called the powerhouse of the cell because of its role in ATP production.
Without cellular respiration, cells would not be able to function efficiently, leading to energy shortages that could disrupt essential life processes.
Where Does Cellular Respiration Occur?
Cellular respiration takes place in two main locations within the cell:
- Cytoplasm
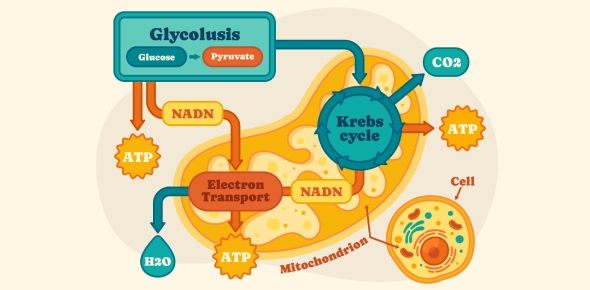
Glycolysis, the first stage of cellular respiration, occurs in the cytoplasm. During glycolysis, glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP and NADH. This step does not require oxygen.
- Mitochondria
The remaining stages, the Krebs cycle and electron transport chain, occur in the mitochondria. The Krebs cycle happens in the mitochondrial matrix, where pyruvate is further processed. The electron transport chain and ATP synthesis take place across the inner mitochondrial membrane, where the majority of ATP is produced. Oxygen is essential for the final step in the electron transport chain.
Take This Quiz :
Why Is Cellular Respiration Important?
Cellular respiration provides the energy necessary for essential functions such as muscle contraction, nerve signaling, and active transport of molecules.
- Energy Production
Cellular respiration generates ATP, which powers essential activities like muscle contraction, nerve signaling, and molecule transport. Without ATP, cells cannot function properly.
- Supports Metabolism
Metabolic reactions require energy to synthesize proteins, enzymes, and other biomolecules. Cellular respiration provides the ATP needed to drive these reactions efficiently.
- Maintains Body Temperature
The process releases heat as a byproduct, helping organisms regulate body temperature. This is especially important for warm-blooded animals to maintain homeostasis.
- Enables Cell Growth and Repair
Cell division, tissue repair, and regeneration rely on ATP. Cellular respiration ensures a continuous energy supply for building and maintaining new cells.
- Facilitates Active Transport
Cells need energy to move substances across membranes, such as pumping ions in nerve cells or absorbing nutrients in the intestines. Cellular respiration provides the required ATP.
- Allows Survival in Different Conditions
In low-oxygen environments, some cells switch to anaerobic respiration to produce ATP, ensuring short-term survival even when oxygen is scarce.
- Essential for Plants and Microorganisms
In plants, cellular respiration releases energy for growth, nutrient transport, and biosynthesis. Microorganisms rely on it to adapt and thrive in diverse environments.
What Are the Types of Cellular Respiration?
There are two types of cellular respiration- aerobic and anaerobic, and they differ in various ways -
| Feature | Aerobic Respiration | Anaerobic Respiration |
| Oxygen Requirement | Aerobic respiration requires oxygen to occur. | Anaerobic respiration does not require oxygen. |
| Location | Aerobic respiration occurs in the cytoplasm (during glycolysis) and in the mitochondria (during the Krebs cycle and electron transport chain). | Anaerobic respiration takes place in the cytoplasm during glycolysis. |
| End Products | The end products of aerobic respiration are carbon dioxide and water. | The end products of anaerobic respiration are lactic acid (in animals) or ethanol and carbon dioxide (in yeast and some bacteria). |
| ATP Yield per Glucose Molecule | Aerobic respiration produces up to 38 ATP molecules per glucose molecule. | Anaerobic respiration produces only 2 ATP molecules per glucose molecule. |
| Efficiency | Aerobic respiration is highly efficient in producing energy. | Anaerobic respiration is less efficient and produces less energy. |
| Process Duration | Aerobic respiration takes longer because it involves multiple stages of breakdown. | Anaerobic respiration is faster as it involves fewer stages. |
| Use in Organisms | Aerobic respiration is the main method of energy production in organisms when oxygen is available. | Anaerobic respiration is used by organisms in low-oxygen conditions, such as during intense exercise or fermentation processes. |
What Are the Stages of Cellular Respiration?
The cellular respiration process occurs in three main stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. Each stage plays a crucial role in breaking down glucose to produce ATP, the energy currency of the cell.
(Alt text - Cellular respiration stages: Glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and electron transport)
- Glycolysis
- Location: Cytoplasm
- Process: Glycolysis is the first step in cellular respiration, where one molecule of glucose (6 carbon atoms) is split into two molecules of pyruvate (3 carbon atoms each). During this process, a small amount of energy is released, forming 2 ATP molecules and 2 NADH molecules. This step does not require oxygen (anaerobic).
- Key Products: 2 ATP, 2 NADH, 2 Pyruvate
- Location: Cytoplasm
- Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
- Location: Mitochondrial Matrix
- Process: Each pyruvate molecule is converted into acetyl-CoA, which enters the Krebs cycle. In this cycle, acetyl-CoA combines with oxaloacetate to form citric acid. Throughout several reactions, energy is transferred to NADH and FADH₂, and a small amount of ATP is produced. Carbon dioxide is released as a byproduct.
- Key Products: 2 ATP, 6 NADH, 2 FADH₂, 4 CO₂ (per glucose molecule)
- Location: Mitochondrial Matrix
- Electron Transport Chain (ETC) and Oxidative Phosphorylation
- Location: Inner Mitochondrial Membrane
- Process: NADH and FADH₂ produced in earlier stages donate electrons to the electron transport chain. As electrons move through protein complexes in the membrane, energy is used to pump protons (H⁺) across the membrane, creating a proton gradient. Oxygen serves as the final electron acceptor, combining with electrons and protons to form water. The proton gradient drives ATP synthase to produce a large amount of ATP.
- Key Products: Approximately 34 ATP, water (H₂O)
- Location: Inner Mitochondrial Membrane
Together, these stages result in the complete breakdown of glucose, producing ATP that powers cellular activities. Oxygen is essential in the later stages to maximize ATP production, making aerobic respiration highly efficient.
Take This Quiz :
Rate this lesson:
 Back to top
Back to top