Bio1a Exam Chapter 2

This quiz covers biomolecules, properties of water, and atoms and elements. It is timed!
- 1.
Glucose, the primary source of energy for a cell, is a type of
- A.
Polypeptide
- B.
Polysaccharide
- C.
Disaccharide
- D.
Monosaccharide
Correct Answer
D. MonosaccharideExplanation
Glucose is a monosaccharide, which means it is a simple sugar consisting of a single sugar unit. As the primary source of energy for cells, glucose is easily broken down and utilized by the body. Polypeptides, polysaccharides, and disaccharides, on the other hand, are larger molecules composed of multiple sugar units and serve different functions in the body.Rate this question:
-
- 2.
The atoms that make up carbohydrates are
- A.
C, H and O
- B.
C, H, O and N
- C.
C and H
- D.
C, H and N
Correct Answer
A. C, H and OExplanation
Carbohydrates are organic compounds composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. These atoms combine in various ratios to form different types of carbohydrates, such as sugars, starches, and fibers. The presence of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms is essential for the formation of the characteristic structure and properties of carbohydrates. Therefore, the correct answer is C, H, and O.Rate this question:
-
- 3.
Lipids are
- A.
Hydrophobic
- B.
Insoluble in water
- C.
Important for energy storage
- D.
All of these
Correct Answer
D. All of theseExplanation
Lipids are hydrophobic, meaning they are unable to dissolve in water. They are also insoluble in water for the same reason. Additionally, lipids are important for energy storage in the body. Therefore, the correct answer is "all of these" as lipids possess all of these characteristics.Rate this question:
-
- 4.
Which of the following is not a function in which lipids play an important role?
- A.
Vision
- B.
Membrane structure
- C.
Chemical signaling
- D.
Storing energy
Correct Answer
A. VisionExplanation
Lipids play an important role in vision as they are a major component of the retina and are involved in the absorption and transport of light. They also contribute to the formation of membrane structures, act as signaling molecules in chemical signaling, and serve as a storage form of energy. Therefore, all the given options are functions in which lipids play an important role.Rate this question:
-
- 5.
You have isolated an unidentified liquid from a sample of beans. You add the liquid to a beaker of water and shake vigorously. After a few minutes, the water and the other liquid separate into two layers. To which class of large biological molecules does the unknown liquid most likely belong?
- A.
Proteins
- B.
Lipids
- C.
Nucleic acids
- D.
Carbohydrates
Correct Answer
B. LipidsExplanation
The correct answer is lipids because lipids are hydrophobic (water-repellent) molecules that tend to separate from water. When the unidentified liquid is added to water and shaken vigorously, the lipids in the liquid will form a separate layer from the water due to their hydrophobic nature. Proteins, nucleic acids, and carbohydrates are generally hydrophilic (water-loving) and would not separate into distinct layers in the same way as lipids.Rate this question:
-
- 6.
Amino acids are the monomers that join together to form
- A.
Carbohydrates
- B.
Lipids
- C.
Proteins
- D.
Nucleic acids
Correct Answer
C. ProteinsExplanation
Amino acids are the building blocks or monomers that combine through peptide bonds to form proteins. Proteins are large, complex molecules that play crucial roles in various biological processes such as enzyme catalysis, cell signaling, and structural support. Each protein has a unique sequence of amino acids, which determines its structure and function. Therefore, the correct answer is proteins.Rate this question:
-
- 7.
Which description BEST fits the class of molecules known as nucleotides?
- A.
A pentose sugar and a purine or pyrimidine
- B.
A phosphate group and an adenine or uracil
- C.
A nitrogenous base and a pentose sugar
- D.
A nitrogenous base, a phosphate group, and a pentose sugar
Correct Answer
D. A nitrogenous base, a phosphate group, and a pentose sugarExplanation
Nucleotides are molecules that make up the building blocks of DNA and RNA. They consist of three main components: a nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, or uracil), a phosphate group, and a pentose sugar (ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA). Therefore, the correct answer is "a nitrogenous base, a phosphate group, and a pentose sugar." This combination of components allows nucleotides to form the backbone of nucleic acids and play a crucial role in genetic information storage and transfer.Rate this question:
-
- 8.
Hemoglobin is a globular protein composed of four polypeptide chains and their associated heme groups. Each polypeptide chain is a string of amino acids. What holds the amino acids together?
- A.
Hydrogen bonds
- B.
Double covalent bonds
- C.
Ionic bonds
- D.
Peptide bonds
Correct Answer
D. Peptide bondsExplanation
Peptide bonds hold the amino acids together in a polypeptide chain. Peptide bonds are formed through a dehydration synthesis reaction between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid. This bond forms a strong covalent linkage between the amino acids, creating the backbone of the protein. Therefore, peptide bonds are responsible for holding the amino acids together in the polypeptide chain of hemoglobin.Rate this question:
-
- 9.
Which organic molecules store the genetic information of a cell?
- A.
Carbohydrates
- B.
Proteins
- C.
Lipids
- D.
Nucleic acids
Correct Answer
D. Nucleic acidsExplanation
Nucleic acids store the genetic information of a cell. They are composed of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid), which carry the instructions for the development, functioning, and reproduction of all living organisms. DNA is found in the nucleus of a cell and contains the hereditary information, while RNA plays a crucial role in protein synthesis. Nucleic acids are responsible for transmitting genetic traits from one generation to the next and are essential for the proper functioning of cells and organisms.Rate this question:
-
- 10.
What is the major purpose of DNA?
- A.
To protect the cells from viruses
- B.
To help in amino acid biosynthesis
- C.
To store genetic information and serve as template to make RNA
- D.
To make carbohydrates during photosynthesis
Correct Answer
C. To store genetic information and serve as template to make RNAExplanation
The major purpose of DNA is to store genetic information and serve as a template to make RNA. DNA contains the instructions for building and maintaining an organism. It carries the genetic code that determines an individual's traits and characteristics. DNA serves as a blueprint for the production of RNA, which is essential for protein synthesis and cellular functioning. DNA also allows for the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next through the process of replication and inheritance.Rate this question:
-
- 11.
The atom is made of 3 subatomic particles. The subatomic particle found in the nucleus with a positive charge is the ___________.
- A.
Electron
- B.
Neutron
- C.
Proton
Correct Answer
C. ProtonExplanation
The question is asking about the subatomic particle found in the nucleus of an atom with a positive charge. The only subatomic particle that fits this description is the proton. Electrons have a negative charge and are found outside the nucleus, while neutrons have no charge and are also found in the nucleus. Therefore, the correct answer is proton.Rate this question:
-
- 12.
The __________ is the smallest unit of matter.
- A.
Element
- B.
Atom
- C.
Molecule
- D.
Electron
Correct Answer
B. AtomExplanation
An atom is the smallest unit of matter that retains the chemical properties of an element. It consists of a nucleus, which contains protons and neutrons, and electrons that orbit the nucleus. Elements are made up of atoms, and atoms combine to form molecules. Therefore, an atom is the correct answer as it is the fundamental building block of matter.Rate this question:
-
- 13.
An _______ bond is a bond in which electrons are transferred.
- A.
Covalent
- B.
Ionic
- C.
Double
Correct Answer
B. IonicExplanation
An ionic bond is a bond in which electrons are transferred. In an ionic bond, one atom donates electrons to another atom, resulting in the formation of positively and negatively charged ions. This transfer of electrons creates a strong electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions, leading to the formation of a stable bond. Covalent bonds, on the other hand, involve the sharing of electrons between atoms, while double bonds refer to a type of covalent bond where two pairs of electrons are shared between atoms.Rate this question:
-
- 14.
An acid has a pH below ______.
- A.
7
- B.
8
- C.
9
- D.
10
Correct Answer
A. 7Explanation
An acid has a pH below 7 because pH is a measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution. Acids have a higher concentration of hydrogen ions, which causes the pH to be lower than 7. A pH of 7 is considered neutral, while pH values below 7 indicate increasing acidity. Therefore, a pH below 7 is characteristic of an acid.Rate this question:
-
- 15.
A base has a ph above _____.
- A.
9
- B.
8
- C.
7
- D.
10
Correct Answer
C. 7Explanation
A base has a pH above 7 because pH is a scale that measures the acidity or alkalinity of a substance. A pH value below 7 indicates acidity, while a pH value above 7 indicates alkalinity. Bases are substances that can accept protons (H+) and decrease the concentration of H+ ions in a solution, making it more alkaline. Therefore, a base will have a pH above 7.Rate this question:
-
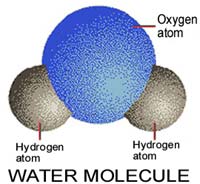
- 16.
Water is made of 1 oxygen molecule and _____ hydrogen atoms.
- A.
3
- B.
2
- C.
1
- D.
5
Correct Answer
B. 2Explanation
Water is made of 1 oxygen molecule and 2 hydrogen atoms. This is because the chemical formula for water is H2O, indicating that there are two hydrogen atoms bonded to one oxygen atom.Rate this question:
-
- 17.
Carbon is an example of a ______.
- A.
Molecule
- B.
Element
- C.
Atom
- D.
Covalent bond
Correct Answer
B. ElementExplanation
Carbon is an example of an element because it is a pure substance made up of only one type of atom. In this case, carbon atoms are the building blocks of the element carbon. Elements cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means, and they are represented on the periodic table by their atomic symbols.Rate this question:
-
- 18.
The water molecule is _________, because there is an uneven distribution of electron within the molecule.
- A.
Uneven
- B.
Weird
- C.
Polar
- D.
Strange
Correct Answer
C. PolarExplanation
The water molecule is polar because there is an uneven distribution of electrons within the molecule. This means that the oxygen atom attracts the shared electrons more strongly than the hydrogen atoms, resulting in a partial negative charge on the oxygen atom and partial positive charges on the hydrogen atoms. This polarity allows water molecules to form hydrogen bonds with each other and with other polar molecules, giving water its unique properties such as high boiling point, surface tension, and ability to dissolve many substances.Rate this question:
-
- 19.
The element found in all living things...______-based life forms.
- A.
Calcium
- B.
Chloride
- C.
Carbon
- D.
Crystals
Correct Answer
C. CarbonExplanation
Carbon is the correct answer because it is an essential element found in all living things. Carbon is the building block of organic molecules, such as proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids, which are crucial for life processes. It forms the backbone of these molecules and enables the diverse structures and functions necessary for life. Other elements like calcium, chloride, and crystals may be present in living organisms, but carbon is the fundamental element that is universally found in all living things.Rate this question:
-
- 20.
The nutrient group that organisms rely on for their energy production
- A.
Proteins
- B.
Lipids
- C.
Carbohydrates
- D.
Nucleic acids
Correct Answer
C. CarbohydratesExplanation
Carbohydrates are the nutrient group that organisms rely on for their energy production. Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which is then used by cells to produce ATP, the main energy currency of the cell. This process occurs through cellular respiration, where glucose is oxidized to release energy. Carbohydrates are found in a variety of foods such as grains, fruits, and vegetables, and they provide a quick and easily accessible source of energy for the body.Rate this question:
-
- 21.
The nutrient group that is used in the composition of enzymes, hormones, and does many different jobs around the cell.
- A.
Proteins
- B.
Lipids
- C.
Carbohydrates
- D.
Nucleic acids
Correct Answer
A. ProteinsExplanation
Proteins are the nutrient group that is used in the composition of enzymes, hormones, and performs various functions within the cell. Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions, while hormones are proteins that regulate bodily functions. Proteins also play a role in cell structure and transport, among other jobs. Lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids have different functions in the body, but they do not perform the same wide range of tasks as proteins. Therefore, proteins are the correct answer for this question.Rate this question:
-
- 22.
The bio-molecular group that carries and passes on the hereditary information of the organism
- A.
Proteins
- B.
Lipids
- C.
Carbohydrates
- D.
Nucleic acids
Correct Answer
D. Nucleic acidsExplanation
Nucleic acids are the bio-molecular group that carries and passes on the hereditary information of the organism. They are responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information in the form of DNA and RNA. Proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates have important roles in the body, but they do not carry or pass on hereditary information like nucleic acids do.Rate this question:
-
- 23.
These bio-molecules are significant features of the cell (plasma) membrane
- A.
Protein and lipid
- B.
Lipid and nucleic acid
- C.
Carbohydrate and nucleic acid
- D.
Nucleic acid and protein
Correct Answer
A. Protein and lipidExplanation
Proteins and lipids are significant features of the cell membrane because they play crucial roles in its structure and function. Proteins are embedded within the lipid bilayer and act as channels, receptors, and transporters, allowing for the movement of molecules in and out of the cell. Lipids, specifically phospholipids, make up the majority of the membrane and provide a barrier that separates the internal and external environments of the cell. Together, proteins and lipids contribute to the selective permeability and integrity of the cell membrane, making them essential components.Rate this question:
-
- 24.
The structural unit ("building block") of a protein is the
- A.
Monosaccharide
- B.
Fatty acid
- C.
Nucleotide
- D.
Amino acid
Correct Answer
D. Amino acidExplanation
Proteins are made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. Amino acids are organic compounds that contain an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a side chain. They are linked together through peptide bonds to form polypeptide chains, which then fold and interact to create the three-dimensional structure of a protein. Therefore, the correct answer is amino acid.Rate this question:
-
- 25.
Which description BEST fits the class of molecules known as nucleotides?
- A.
A pentose sugar and a purine or pyrimidine
- B.
A phosphate group and an adenine or uracil
- C.
A nitrogenous base and a pentose sugar
- D.
A nitrogenous base, a phosphate group, and a pentose sugar
Correct Answer
D. A nitrogenous base, a phosphate group, and a pentose sugarExplanation
Nucleotides are molecules that make up the building blocks of DNA and RNA. They consist of three components: a nitrogenous base, a phosphate group, and a pentose sugar. The nitrogenous base can be either a purine (adenine or guanine) or a pyrimidine (cytosine, thymine, or uracil). The phosphate group provides a negative charge and helps to link nucleotides together to form the DNA or RNA strand. The pentose sugar, usually ribose or deoxyribose, provides the backbone of the nucleotide. Therefore, the description that BEST fits nucleotides is "a nitrogenous base, a phosphate group, and a pentose sugar."Rate this question:
-
- 26.
A group of atoms bound together
- A.
Proton
- B.
Molecule
- C.
Atom
- D.
Compound
Correct Answer
B. MoleculeExplanation
A molecule is a group of atoms bound together by chemical bonds. It is the smallest unit of a compound that retains the chemical properties of that compound. In a molecule, atoms are held together by covalent bonds, which involve the sharing of electrons between atoms. Therefore, a molecule is the correct answer as it describes the concept of a group of atoms bound together.Rate this question:
-
- 27.
A pure substance made up of only one kind of atom
- A.
Molecule
- B.
Compound
- C.
Element
- D.
Isotope
Correct Answer
C. ElementExplanation
An element is a pure substance made up of only one kind of atom. It cannot be broken down into simpler substances and retains its unique properties. Unlike compounds, which are made up of different types of atoms bonded together, elements consist of identical atoms. Molecules, on the other hand, can be made up of either one or multiple types of atoms bonded together. Isotopes, while also consisting of only one type of atom, have different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei, resulting in variations in atomic mass.Rate this question:
-
- 28.
All of these are major organic compounds except
- A.
Carbohydrates
- B.
Lipids
- C.
Proteins
- D.
Acids
Correct Answer
D. AcidsExplanation
Acids are not considered major organic compounds. While they are organic compounds, they are not classified as major because they do not play as significant of a role in biological processes as carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. Acids are more commonly known for their role in chemical reactions and as components of various substances, but they are not as essential to biological systems as the other three options listed.Rate this question:
-
- 29.
Forms wen atoms that share their outer energy fill up and thus become stable
- A.
Covalent bond
- B.
Hydrogen bond
- C.
Ionic bond
- D.
Chemical bond
Correct Answer
A. Covalent bondExplanation
A covalent bond is formed when atoms share their outer energy levels to achieve stability. In this type of bond, electrons are shared between atoms, creating a strong bond. This sharing of electrons allows both atoms to fill up their outer energy levels and become stable. Covalent bonds are commonly found in molecules composed of nonmetals.Rate this question:
-
- 30.
Ionic bonds are
- A.
Bonds to form atoms
- B.
When atom gains or loses electrons in its outer energy level
- C.
When atoms break apart to form new molecules
- D.
Protons are shared to become more stable
Correct Answer
B. When atom gains or loses electrons in its outer energy levelExplanation
Ionic bonds are formed when an atom gains or loses electrons in its outer energy level. This occurs when atoms with different electronegativities come together, causing one atom to transfer electrons to the other. This transfer creates ions with opposite charges, which are then attracted to each other and form an ionic bond. This type of bond typically occurs between metals and nonmetals and results in the formation of stable compounds.Rate this question:
-
- 31.
Water is a
- A.
Isotope
- B.
Solvent
- C.
Anions
- D.
Buffer
Correct Answer
B. SolventExplanation
Water is considered a solvent because it has the ability to dissolve a wide range of substances. This is due to its polar nature, where the oxygen atom is slightly negative and the hydrogen atoms are slightly positive. This polarity allows water molecules to attract and surround ions and other polar molecules, breaking them apart and dispersing them throughout the solution. Water's solvent properties make it essential for many biological and chemical processes, as it allows for the transportation of nutrients, the dissolution of waste products, and the facilitation of chemical reactions.Rate this question:
-
- 32.
Water molecules dissociate to form equal amounts of
- A.
H+(hydrogen ion) and OH- ( hydroxide ion)
- B.
H+/OH- in favor of H+
- C.
NaCl---Na+
Correct Answer
A. H+(hydrogen ion) and OH- ( hydroxide ion)Explanation
Water molecules have the ability to dissociate into H+ (hydrogen ion) and OH- (hydroxide ion) in equal amounts. This is due to the self-ionization of water, where a small fraction of water molecules naturally break apart into these ions. The equilibrium between H+ and OH- is maintained in favor of H+ because water is a weak acid. NaCl, on the other hand, dissociates completely into Na+ and Cl- ions when dissolved in water. Therefore, the correct answer is H+ (hydrogen ion) and OH- (hydroxide ion).Rate this question:
-
- 33.
Increases the hydrogen ion (H+) concentration of a solution by dissociating to release H+
- A.
Base
- B.
Salt
- C.
Acid
- D.
WAter
Correct Answer
C. AcidExplanation
An acid is a substance that increases the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution by dissociating and releasing H+. This increase in H+ concentration makes the solution more acidic. Therefore, the given statement correctly describes an acid.Rate this question:
-
- 34.
Type response below
- 35.
What is the atomic number for carbon?
- A.
Six
- B.
Four
- C.
Two
Correct Answer
A. SixExplanation
The atomic number of an element represents the number of protons in the nucleus of its atom. Carbon has an atomic number of six, which means it has six protons in its nucleus. This determines its unique chemical properties and its position in the periodic table.Rate this question:
-
- 36.
How many valence electrons do carbon atoms have?
- A.
Two
- B.
Six
- C.
Four
- D.
Zero
Correct Answer
C. FourExplanation
Carbon atoms have four valence electrons. Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom and are involved in chemical bonding. Carbon has four valence electrons because it is located in Group 14 of the periodic table, which means it has four electrons in its outermost energy level. These valence electrons allow carbon to form covalent bonds with other atoms, enabling it to form a wide variety of compounds.Rate this question:
-
- 37.
What is a chemical bond?
- A.
A force that holds branched bonds together
- B.
A force that holds chemical experiments together
- C.
A force that hods two carbons together
- D.
A force that holds two atoms together
Correct Answer
D. A force that holds two atoms togetherExplanation
A chemical bond is a force that holds two atoms together. Chemical bonds are formed when atoms share or transfer electrons in order to achieve a more stable electron configuration. This force is responsible for the formation of molecules and compounds, as it creates a strong attraction between the atoms involved.Rate this question:
-
- 38.
WITHIN the water molecules, what type of bond occurs?
Correct Answer
covalent, a covalent bond, covalent bondExplanation
Water molecules are composed of two hydrogen atoms bonded to one oxygen atom. This bonding occurs through the sharing of electrons between the atoms, which is known as a covalent bond. In a covalent bond, the atoms involved share electrons in order to achieve a stable electron configuration. Therefore, within water molecules, covalent bonds occur between the hydrogen and oxygen atoms.Rate this question:
- 39.
What type of bond occurs BETWEEN water molecules?
Correct Answer
hydrogen, hydrogen bond, a hydrogen bondExplanation
Hydrogen bonds occur between water molecules. These bonds are formed when the slightly positive hydrogen atom of one water molecule is attracted to the slightly negative oxygen atom of another water molecule. This attraction is due to the difference in electronegativity between hydrogen and oxygen. Hydrogen bonds are relatively weak compared to covalent or ionic bonds, but they are essential for many of water's unique properties, such as its high boiling point, surface tension, and ability to dissolve many substances.Rate this question:
- 40.
Water molecules are _______________ and stick together. Is this property due to hydrogen bonding or to polarity of water molecules?
Correct Answer
cohesive; hydrogen bondingExplanation
The property of water molecules sticking together is due to hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonding occurs when the hydrogen atom in one water molecule is attracted to the oxygen atom in another water molecule. This attraction creates a cohesive force that allows water molecules to stick together. The polarity of water molecules, with the oxygen atom being slightly negative and the hydrogen atoms being slightly positive, also contributes to this property. However, it is primarily the hydrogen bonding that is responsible for the cohesive nature of water molecules.Rate this question:
- 41.
A(n) ____________ gives off hydrogen ions in a solution while a(n)__________ gives off hydroxide ions.
Correct Answer
acid; baseExplanation
An acid is a substance that releases hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution, while a base is a substance that releases hydroxide ions (OH-) in a solution. This is a fundamental concept in chemistry known as the Arrhenius theory of acids and bases. Acids and bases are considered to be opposites of each other, with acids providing H+ ions and bases providing OH- ions.Rate this question:
- 42.
What does a buffer do to prevent rapid changes in pH?
Correct Answer
It takes up extra hydrogen or hydroxide ions., It takes up extra hydroxide or hydrogen ions.Explanation
A buffer is a solution that resists changes in pH by absorbing or releasing hydrogen (H+) or hydroxide (OH-) ions. When the pH of a solution increases, the buffer takes up extra hydrogen ions to prevent a rapid increase in pH. Similarly, when the pH decreases, the buffer takes up extra hydroxide ions to prevent a rapid decrease in pH. Therefore, the buffer acts as a stabilizing agent, maintaining the pH of a solution within a narrow range.Rate this question:
- 43.
Organic molecules are large in size and are called ______________.
Correct Answer
macromolecules, macromoleculeExplanation
Organic molecules are often large in size due to the presence of multiple carbon atoms bonded together, along with other elements such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and others. These large-sized organic molecules are commonly referred to as macromolecules. Macromolecules can include various types of biomolecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids. These macromolecules play crucial roles in biological processes and are essential for the structure, function, and regulation of cells and organisms. Therefore, the term "macromolecules" accurately describes the large size of organic molecules.Rate this question:
- 44.
Macromolecules are built of smaller units, called __________.
Correct Answer
subunits, subunitExplanation
Macromolecules are large molecules made up of smaller units known as subunits. These subunits are the building blocks of macromolecules and are responsible for their structure and function. The term "subunits" refers to multiple smaller units, while "subunit" refers to a single smaller unit. Therefore, both "subunits" and "subunit" are correct answers to the question.Rate this question:
- 45.
List the four main elements in the human body.
Correct Answer
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogenExplanation
The human body is primarily composed of four main elements: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. These elements are essential for various biological processes and are found in abundance in the human body. Carbon forms the backbone of organic molecules, while hydrogen and oxygen are crucial components of water and many biomolecules. Nitrogen is a key element in proteins and nucleic acids, which are fundamental for cellular function and genetic information. Overall, these four elements play vital roles in maintaining the structure and function of the human body.Rate this question:
- 46.
______________ of an element are atoms that differ in their number of neutrons.
Correct Answer
isotopes, IsotopesExplanation
Isotopes are atoms of an element that have the same number of protons but differ in their number of neutrons. This difference in neutron count results in isotopes having different atomic masses. Therefore, the correct answer is "isotopes, Isotopes."Rate this question:
- 47.
In a triple bond, how many electrons are shared?
Correct Answer
six, 6Explanation
In a triple bond, there are six electrons shared between the two atoms. This is because a triple bond consists of three pairs of electrons being shared, with each pair consisting of two electrons. Therefore, the total number of electrons shared in a triple bond is six.Rate this question:
- 48.
What does our body use glucose as?
Correct Answer
an immediate source of energy, source of energy, a source of energyExplanation
Glucose is used by our body as an immediate source of energy. It is the primary fuel for our brain, muscles, and other tissues. Additionally, glucose serves as a source of energy for various metabolic processes in the body. It is broken down through cellular respiration to produce ATP, which is the energy currency of cells. Therefore, glucose can be described as an immediate source of energy and a source of energy in general.Rate this question:
- 49.
Triglycerides are formed from one ______________ and three ________________ molecules.
Correct Answer
glycerol; fatty acidExplanation
Triglycerides are formed from one molecule of glycerol and three molecules of fatty acid. Glycerol is a three-carbon alcohol that serves as the backbone of triglycerides, while fatty acids are long chains of carbon and hydrogen atoms. The glycerol molecule combines with the three fatty acid molecules through ester bonds, resulting in the formation of triglycerides. This structure allows triglycerides to store energy in the body and serve as a major component of dietary fats and oils.Rate this question:
- 50.
The nucleic acid ____ stores the genetic info for the cell.
Correct Answer
DNAExplanation
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a type of nucleic acid that stores the genetic information for the cell. It is found in the nucleus of the cell and is composed of two strands of nucleotides that form a double helix structure. DNA contains the instructions for building and maintaining an organism, and it carries all the information needed for the cell to function and reproduce. This genetic information is passed on from generation to generation and is responsible for the inheritance of traits.Rate this question:
Quiz Review Timeline +
Our quizzes are rigorously reviewed, monitored and continuously updated by our expert board to maintain accuracy, relevance, and timeliness.
-
Current Version
-
Mar 19, 2023Quiz Edited by
ProProfs Editorial Team -
Jul 06, 2017Quiz Created by
Alexander Angeles