In contemporary multilevel machines, what is the third level?
What are the three properties that you can get from a RAID?
Modems or transmission lines that can only transmit in one direction...
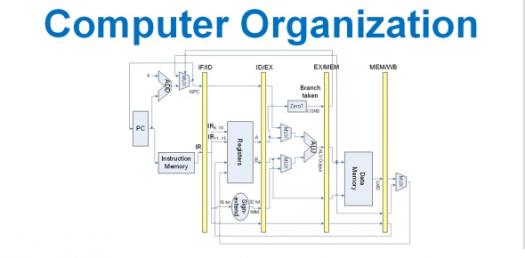
List in numerical order what each component is. Separate your answers...
What eliminates noise and only has two states?
List in numerical order what each component is. Separate your answers...
A system where numbering begins with the least significant bit is...
Which computer generation saw transistors (1955-1965)?
What does RISC stand for?
What translator compiles all of the source code before the execution...
What does CISC stand for?
What does DMA stand for?
Which computer generation saw integrated circuits (1965-1980)?
What was the biggest enemy of computers in the first generation?
What states that the number of transistors that can be put in a chip...
What forces the CPU to immediately suspend running its current program...
What is also known as a storage area?
Which computer generation saw vacuum tubes (1945-1955)?
What is a collection of parallel wires used for transmitting
...
What is a bit that is added to ensure that the number of bits with the...
Which computer generation saw very large scale integration (1980 -...
What does RAID stand for?
What checks the interrupt for errors, takes any special actions...
What is it called when no I/O is in progress and the CPU has all the...
When you are transmitting data, there are three basic parameters that...
What is a set of tracks at a given radial position called?
How fast a signal goes up and down is it's ___________?
The ability of two different entities to talk to each other at the...
In contemporary multilevel machines, what is the fourth level?
How high and low a signal goes is it's ___________?
What has a temporal and spacial aspect to it?
In contemporary multilevel machines, what is level zero?
A system where numbering begins at the "high order" end is called?
In contemporary multilevel machines, what is the fifth level?
When you change the sin waves ending and beginning of a signal, it is...
Lines that can only transmit in one direction are called ___________?
Which translator requires source code to execute?
What acts as an interface between the I/O controllers and memory by...
The circular sequence of bits written as the disk makes a complete...
What do you call the fixed length portions that a track is divided...
What is the assembly line style for processing instructions
...
In contemporary multilevel machines, what is the second level?
In contemporary multilevel machines, what do you use to get from one...
What translator executes the program as it translates?
What is the gateway between the external device and the internal...
Instead of pulling a particular address from memory, you pull a...
What is the refractive surface of optical media that scatters light...
Which computer generation saw mechanical computers (1642-1945)?
What architecture is in almost every one of today's computing...
What are the main types of systems that are used to determine...
How many levels are there in contemporary multilevel machines?
What is SIMD?
Name the two types of translators.
In contemporary multilevel machines, what is the first level?
Please list the components in numerical order separated by a comma and...
The following is an example of what type of architecture?
What is also known as an emulator and allows for other software
...
What is used to decide which goes first in the case that the CPU and...
What is the reflective surface of optical media that reflects light to...
What does a CPU do?