Nervous System Quiz: What Do You Know About The Human Brain?
(457).jpg)
Check out this nervous system quiz and find out what do you know about the human brain. This test will clear out all your doubts regarding it. The nervous system is the major controlling and complex part of the body that coordinates all its actions and information throughout the body. We've created this exciting quiz to check your knowledge about your brain. Do you think you can pass this quiz? Play it now and prove it to us. All the best!
- 1.
ANS system innervates .... in all tissues
- A.
Smooth muscle
- B.
Skeletal muscle
- C.
Nervous tissue
- D.
Striated muscle
Correct Answer
A. Smooth muscleExplanation
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) innervates smooth muscle in all tissues. Smooth muscle is found in various organs and structures throughout the body, such as the digestive system, blood vessels, and reproductive organs. The ANS controls involuntary functions, including the contraction and relaxation of smooth muscle. This allows for the regulation of processes like digestion, blood flow, and reproductive functions. Skeletal muscle, on the other hand, is innervated by the somatic nervous system and is under voluntary control. Nervous tissue refers to the neurons and supporting cells that make up the nervous system, while striated muscle refers to skeletal and cardiac muscle, which have a striped appearance under a microscope.Rate this question:
-
- 2.
At the ganglion where Visceral motor efferent fibers synapse what neurotransmitter is used
- A.
Acetylcholine
- B.
Nicotinic
- C.
Norepinephrine
- D.
Epinephrine
Correct Answer
A. AcetylcholineExplanation
At the ganglion where Visceral motor efferent fibers synapse, the neurotransmitter used is acetylcholine. Acetylcholine is the primary neurotransmitter released by the preganglionic neurons of the autonomic nervous system. It binds to nicotinic receptors on the postganglionic neurons, leading to the transmission of signals from the preganglionic to the postganglionic neurons. This allows for the relay of information and control of various bodily functions by the autonomic nervous system.Rate this question:
-
- 3.
Parasympathetic ganglia are
- A.
Shorter with local control
- B.
Longer local control
- C.
Shorter with non-specific control
- D.
Cause whole system effect
Correct Answer
A. Shorter with local controlExplanation
Parasympathetic ganglia are shorter with local control because they are located closer to the target organs they innervate. This allows for more precise and specific control over the functions of these organs. Additionally, the parasympathetic nervous system primarily regulates rest and digest activities, which require localized control rather than whole system effects.Rate this question:
-
- 4.
Another name for parasympathetic is
- A.
Cholinergic
- B.
Adrenergic
- C.
Cranial sacral
- D.
Muscorinic
Correct Answer(s)
A. Cholinergic
C. Cranial sacralExplanation
The parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for rest and digest functions. It is often referred to as the cranial sacral division because its preganglionic fibers originate from the cranial nerves and the sacral region of the spinal cord. The neurotransmitter used by the parasympathetic system is acetylcholine, which is why it is also known as cholinergic. Therefore, both cholinergic and cranial sacral are alternative names for the parasympathetic nervous system.Rate this question:
-
- 5.
You are likely to see parasympathetic nerves
- A.
Top of spinal cord and bottom
- B.
Middle spinal cord
- C.
Thorasic lumbar
- D.
Near the heart
Correct Answer
A. Top of spinal cord and bottomExplanation
area where breathing and digestion occurRate this question:
-
- 6.
Sympathetic nerves are likely to be found
- A.
Along blood vessels
- B.
The top and the bottom of the spinal cord
- C.
The brain
- D.
The lungs
Correct Answer
A. Along blood vesselsExplanation
Sympathetic nerves are likely to be found along blood vessels because they are responsible for regulating the constriction and dilation of blood vessels. These nerves help control blood flow and blood pressure by signaling the smooth muscles in the walls of blood vessels to contract or relax. Therefore, it is logical for sympathetic nerves to be located alongside blood vessels to efficiently transmit these signals and regulate the circulatory system.Rate this question:
-
- 7.
Sympathetic nervous system does all BUT
- A.
Profuse thin secretion
- B.
Urine retention
- C.
Bronchodilate
- D.
Increase HR
Correct Answer
A. Profuse thin secretionExplanation
The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for the "fight or flight" response in the body, which involves various physiological changes to prepare for potential danger. One of these changes is an increase in heart rate to pump more blood to the muscles. Additionally, the sympathetic nervous system causes bronchodilation, which allows for increased airflow to the lungs. However, it does not control the production of profuse thin secretion, which is likely regulated by other systems or factors in the body. Urine retention is controlled by the parasympathetic nervous system, which is the opposite of the sympathetic system.Rate this question:
-
- 8.
A pt shows up to your clinic with a low HR, lungs constricted, lots of urine and stool, watery saliva what do you do
- A.
Turn off cholinergic responce
- B.
Give epinephrine
- C.
Stop adrenal gland
- D.
Give adrenalin
Correct Answer
A. Turn off cholinergic responceExplanation
The given correct answer suggests turning off the cholinergic response. This is because the symptoms described in the question, such as low heart rate, constricted lungs, excessive urine and stool, and watery saliva, are indicative of excessive cholinergic activity. By turning off the cholinergic response, the excessive stimulation can be reduced, leading to an improvement in the patient's condition.Rate this question:
-
- 9.
The pathway of sympathetic/ parasympathetic
- A.
CNS--> nerves (hitchhike or splanchnic)--> ganglia (chain or visceral)--> neurotransmitters--> receptors on smooth muscle
- B.
CNS--> ganglia (chain or visceral)--> nerves (hitchhike or splanchnic)--> neurotransmitters --> receptors on smooth muscle
- C.
Nerves (hitchhike or splanchnic) --> ganglia ( chain or visceral) --> CNS --> neurotransmitters --> receptors on smooth muscle
- D.
Receptors on smooth muscle --> CNS --> neurotransmitters --> ganglia (chain or visceral)--> nerves
Correct Answer
A. CNS--> nerves (hitchhike or splanchnic)--> ganglia (chain or visceral)--> neurotransmitters--> receptors on smooth muscleExplanation
The correct answer is the pathway of sympathetic/parasympathetic: CNS -> nerves (hitchhike or splanchnic) -> ganglia (chain or visceral) -> neurotransmitters -> receptors on smooth muscle. This pathway describes the sequence of events in the autonomic nervous system, where signals from the central nervous system (CNS) are transmitted through nerves to ganglia, where neurotransmitters are released and bind to receptors on smooth muscle, resulting in the desired response.Rate this question:
-
- 10.
Chain ganglia are associated with
- A.
Sympathetic
- B.
Visceral
- C.
Parasympathetic
- D.
Cholinergic
Correct Answer
A. SympatheticExplanation
Chain ganglia are associated with the sympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for the "fight or flight" response, which prepares the body for stressful situations. Chain ganglia are clusters of nerve cell bodies located on either side of the spinal cord, and they play a crucial role in transmitting signals between the central nervous system and various target organs. These ganglia are involved in regulating various bodily functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, and digestion, which are all part of the sympathetic nervous system's response to stress.Rate this question:
-
- 11.
Final pathway within smooth muscle are
- A.
Calcium channel
- B.
Sodium channel
- C.
Potassium channel
- D.
Ganglion
Correct Answer
A. Calcium channelExplanation
Smooth muscle contraction is regulated by the influx of calcium ions into the muscle cells. Calcium channels in the cell membrane allow calcium ions to enter the cell, triggering muscle contraction. The other options, sodium and potassium channels, are involved in the generation and propagation of action potentials in nerve and muscle cells, but they are not specifically associated with smooth muscle contraction. Ganglion refers to a cluster of nerve cell bodies, which is not directly related to the final pathway within smooth muscle. Therefore, the correct answer is calcium channel.Rate this question:
-
- 12.
What is NOT a kind of ANS ganglia
- A.
Splanchnic abdominal ganglia
- B.
Sympathetic chain ganglia
- C.
Sympathetic collateral (visceral) ganglia
- D.
Parasypathetic end-organ ganglia
Correct Answer
A. Splanchnic abdominal gangliaExplanation
The splanchnic abdominal ganglia are not a kind of ANS ganglia. The sympathetic chain ganglia, sympathetic collateral (visceral) ganglia, and parasympathetic end-organ ganglia are all examples of ANS ganglia.Rate this question:
-
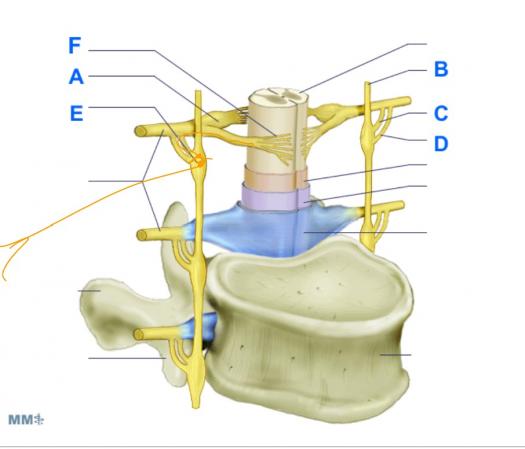
- 13.
What is most likely to be found in the are marketed E
- A.
Sympathetic post-ganglion neuron cell bodies
- B.
Parasympathetic pre-ganglionic neuron cell bodies
- C.
Somatic motor neuron cell bodies
- D.
Somatic sensory neuron cell bodies
Correct Answer
A. Sympathetic post-ganglion neuron cell bodiesExplanation
The most likely answer to be found in the area "E" is sympathetic post-ganglion neuron cell bodies. This is because sympathetic post-ganglion neurons are responsible for transmitting signals from the ganglia to the effector organs in the sympathetic nervous system. The other options, such as parasympathetic pre-ganglionic neuron cell bodies, somatic motor neuron cell bodies, and somatic sensory neuron cell bodies, are not typically found in this area.Rate this question:
-
- 14.
Visceral sensory is processed
- A.
Travel up chain ganglia
- B.
Dorsal root ganglia
- C.
Paravertebral ganglia
- D.
Nerve plexus
Correct Answer
A. Travel up chain gangliaExplanation
The correct answer is "travel up chain ganglia." This is because visceral sensory information is processed and transmitted through a series of ganglia, starting from the dorsal root ganglia, then passing through the paravertebral ganglia, and finally reaching the nerve plexus. The chain ganglia play a crucial role in relaying the sensory information from the organs to the central nervous system for further processing and response.Rate this question:
-
- 15.
Lateral horn is devoted mostly to
- A.
Autonomic (visceral) motor cell body
- B.
LMN
- C.
Interneuron somatic sensory neuron
- D.
Somatic motor neuron
Correct Answer
A. Autonomic (visceral) motor cell bodyExplanation
The lateral horn is primarily responsible for housing autonomic (visceral) motor cell bodies. These cell bodies are involved in controlling and regulating involuntary bodily functions, such as digestion, heart rate, and respiration. The autonomic nervous system, which includes the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions, relies on these motor cell bodies in the lateral horn to transmit signals to various organs and tissues in the body. Therefore, the correct answer is autonomic (visceral) motor cell body.Rate this question:
-
- 16.
Damage to the spine on the lateral and ventral horn would cause
- A.
LMN and visceral motor symptoms
- B.
UMN and sensory motor symotoms
- C.
Somatic sensory symptoms
- D.
Visceral sensory symptoms
Correct Answer
A. LMN and visceral motor symptomsExplanation
Damage to the spine on the lateral and ventral horn would cause LMN and visceral motor symptoms. The lateral and ventral horns of the spinal cord are responsible for housing the cell bodies of lower motor neurons (LMN) that innervate muscles and control movement. Damage to these areas would result in the impairment of these LMNs, leading to muscle weakness, atrophy, and decreased reflexes. Additionally, the ventral horn also contains preganglionic autonomic neurons that control the visceral organs. Therefore, damage to the spine in these regions would also cause dysfunction in the autonomic nervous system, resulting in visceral motor symptoms.Rate this question:
-
- 17.
Adrenal medulla releases
- A.
Epinephrine and norepinephrine
- B.
Acetylecoline
- C.
Nicitine
- D.
Ligands
Correct Answer
A. Epinephrine and norepinephrineExplanation
The adrenal medulla releases epinephrine and norepinephrine. These are hormones that are responsible for the body's "fight or flight" response to stress. They increase heart rate, blood pressure, and blood sugar levels, preparing the body for immediate action. Acetylcholine and nicotine are not released by the adrenal medulla, and ligands are molecules that bind to receptors.Rate this question:
-
- 18.
Cholinergic
- A.
Gives out acetylcholine and acts parasympathetic
- B.
Gives out acetylcholine and acts sympathetic
- C.
Pours out epinephrine and norepinephrine
- D.
Pours out dopamine
Correct Answer
A. Gives out acetylcholine and acts parasympatheticExplanation
Cholinergic refers to the neurons or receptors that release or respond to acetylcholine. Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that is involved in the parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for rest and digest functions. Therefore, the correct answer is that cholinergic neurons give out acetylcholine and act on the parasympathetic nervous system.Rate this question:
-
Quiz Review Timeline +
Our quizzes are rigorously reviewed, monitored and continuously updated by our expert board to maintain accuracy, relevance, and timeliness.
-
Current Version
-
Mar 31, 2023Quiz Edited by
ProProfs Editorial Team -
Mar 21, 2022Quiz Created by
Alfredhook3
 Back to top
Back to top