Ever taken a quiz where the questions were so vague that you had no idea what was being asked? Or one where the right answer practically jumped off the page? These common quizzing mistakes can make assessments confusing, frustrating, and ineffective.
A good quiz should test knowledge in a fair and meaningful way, but small mistakes in wording, structure, or answer choices can undermine its purpose.
If your quizzes aren’t giving you useful insights, it might be time to fix these issues.
Top 10 Common Quizzing Mistakes With Examples
Here are ten frequent errors in creating quiz questions, along with advice on how to prevent them:
1. Asking Vague or Overly Broad Questions
A quiz question should be clear and direct. If a learner reads it and wonders, “What exactly do they mean?”—that’s a red flag. When questions are too broad, learners might interpret them in different ways, leading to inconsistent answers.
Worse, some may pick the correct option simply because it covers everything rather than demonstrating real understanding.
🔴 Example of a vague question:
How can employees improve communication at work?
A. By listening
B. By speaking clearly
C. By being respectful
D. All of the above
Since all answers are technically correct, the question doesn’t assess whether someone actually understands effective communication strategies.
✅ How to fix it:
Reword the question to focus on one key concept so that there’s only one correct answer.
What is the most effective first step in resolving a workplace miscommunication?
A. Clarify intent and seek understanding
B. Avoid discussing the issue
C. Involve multiple colleagues for advice
D. Ignore the misunderstanding and move on
Now, the question is precise and requires actual thought rather than process-of-elimination guessing.
💡Pro Tip:
If you need help crafting specific questions, ProProfs’ AI quiz maker can generate high-quality questions in seconds, saving you time and effort!
2. Writing Trick Questions That Mislead Learners
A quiz is supposed to test knowledge, not patience. Trick questions frustrate learners because they feel like traps rather than fair assessments. Instead of evaluating understanding, these questions create unnecessary confusion, making people second-guess everything.
🔴 Example of a trick question:
Which of the following is NOT a reason why employees leave a company?
A. Lack of career growth
B. Poor management
C. Job satisfaction
D. Low compensation
That sneaky “NOT” completely flips the logic, increasing the chances of misreading the question rather than testing knowledge.
✅ How to fix it:
Phrase questions in a way that keeps things clear and prevents unnecessary confusion.
What is a common reason employees leave a company?
A. Lack of career advancement
B. Strong leadership
C. Competitive salaries
D. Supportive work culture
This version keeps the focus on knowledge, not tricky wording.
3. Using Answer Choices That Are Too Obvious
This one might be the most common quizzing mistake of all!
A quiz question should make learners think. If the correct answer sticks out like a neon sign, the question isn’t really testing anything. If one option is way more logical than the others, learners don’t even need to read the question carefully—they can just guess. That’s not a good thing.
🔴 Example of an obvious answer:
What should you do if you see smoke coming from an office building?
A. Call emergency services
B. Run inside
C. Do nothing and keep working
It’s obvious that “A” is correct, making this question completely pointless.
✅ How to fix it:
Make all choices sound reasonable so learners actually have to think.
What is the safest first step when encountering a workplace fire emergency?
A. Follow emergency exit procedures
B. Call a colleague for advice
C. Continue working unless an alarm sounds
Now, only someone who truly understands fire safety will pick the correct answer.
4. Providing Inconsistent or Unbalanced Answer Choices
If the correct answer is way longer or more detailed than the others, it practically gives itself away. Learners might start selecting the longest answer by default, assuming it must be correct. That’s not the way a quiz should work.
🔴 Example of an unbalanced answer set:
What is a key leadership trait?
A. Confidence
B. Communication
C. The ability to effectively inspire employees, foster innovation, and drive the company toward achieving long-term success
That last option sticks out like a sore thumb. Even if someone isn’t sure, they’ll probably pick it just because it looks right.
✅ How to fix it:
Keep all answers consistent in length and structure to avoid making the correct one too obvious.
- A. Confidence
- B. Strategic thinking
- C. Decision-making
Now, learners have to rely on their actual knowledge, not just answer length.
5. Overloading Questions with Too Much Information
A quiz question isn’t the place for storytelling. If there’s too much unnecessary detail, learners get lost in the wording rather than focusing on what’s actually being asked. When someone has to read a question three times just to figure out the point, that’s a problem.
🔴 Example of an overloaded question:
An organization is implementing a new software system, and employees must complete training before using it. However, some employees are struggling to grasp the system’s complexity, leading to frustration. What should the company do to improve adoption rates?
✅ How to fix it:
Keep the wording clear and direct without unnecessary backstory.
What is an effective strategy for improving software adoption among employees?
This version gets straight to the point, making it easier to answer.
6. Failing to Include Clear Instructions
Ever taken a quiz where you weren’t exactly sure what the question was asking you to do? It’s frustrating. If learners don’t understand the instructions, they might waste time figuring out the format instead of answering the actual question.
🔴 Example of unclear instructions:
Sort the following leadership traits.
Sort them how? Alphabetically? By importance? In order of effectiveness?
✅ How to fix it:
Tell learners exactly what they need to do.
Arrange the following leadership traits from most to least important in decision-making.
Clear instructions eliminate confusion, making the quiz smoother to take.
7. Ignoring Spelling and Grammar Mistakes
A quiz should look polished. If a question has typos or poor grammar, it can make the whole quiz feel unprofessional. Worse, it might confuse learners and cause them to misinterpret the question. Even small mistakes can create doubt and frustration, especially when someone gets a question wrong due to unclear wording.
🔴 Example of a grammar/spelling mistake:
Wich of the following impact employee moral the most?
That’s just sloppy! A simple spelling mistake distracts from the content and makes the quiz seem rushed.
✅ How to fix it:
Always proofread carefully before publishing a quiz.
Which of the following impacts employee morale the most?
Now, the question looks professional and won’t cause unnecessary confusion.
8. Using Too Many Answer Choices
More options aren’t always better. If a question has too many answer choices, it can overwhelm learners and make it harder to process the information. Instead of thinking critically, they might just pick something at random.
🔴 Example of too many answer choices:
Which of the following is a primary cause of the American Revolution?
A. High taxation without representation
B. The invention of the steam engine
C. Conflict over land ownership with Native American tribes
D. The influence of the French Revolution
E. The decline of British naval power
F. Disagreements over the Articles of Confederation
With six answer choices, this question forces learners to spend extra time sorting through distractions, some of which are historically inaccurate. The excessive options make the quiz harder than it needs to be.
✅ How to fix it:
Limit choices to four well-thought-out options that challenge the learner without overwhelming them.
Which of the following is a primary cause of the American Revolution?
A. High taxation without representation
B. The invention of the steam engine
C. The influence of the French Revolution
D. Disagreements over the Articles of Confederation
Now, the correct answer (A) stands out a bit, while the remaining choices are plausible but incorrect upon deeper analysis.
9. Repeating the Same Question Type Too Often
Using only multiple-choice questions (MCQs) in a quiz can make it less engaging and limit how deeply learners interact with the material. While MCQs are effective for testing recognition and recall, they don’t always encourage critical thinking or application. A well-rounded quiz should include a mix of question types to keep learners actively engaged and assess different levels of understanding.
🔴 Example of a repetitive question structure:
Which of the following is an example of effective leadership?
A. Clear communication
B. Ignoring feedback
C. Avoiding team collaboration
Which of the following improves workplace productivity?
A. Delegation
B. Micromanagement
C. Lack of direction
Which of the following is a key component of workplace motivation?
A. Recognition and rewards
B. Inconsistent policies
C. Lack of job security
Since every question follows the same format, the quiz lacks variety, which can make it feel repetitive and one-dimensional.
✅ How to fix it:
Introduce different question formats to assess knowledge in multiple ways:
- True/False: A leader should always ignore employee concerns to maintain authority.
- Fill-in-the-blank: A company’s long-term strategy is often defined by its ______ vision.
- Scenario-based: An employee is struggling to meet deadlines due to workload. What should their manager do?
By varying question types, quizzes become more engaging, encourage deeper thinking, and provide a more complete assessment of knowledge.
Watch: Question Types for Online Learning & Assessment
10. Not Providing Feedback After Questions
A quiz isn’t just about getting answers right or wrong—it’s a learning opportunity. If a quiz simply marks an answer incorrect without any explanation, the learner doesn’t gain any insight into their mistakes. Without feedback, they might keep repeating the same errors without knowing what to fix.
🔴 Example of a quiz with no feedback:
After answering a question, the learner only sees:
❌ Incorrect
✔️ Correct
That doesn’t help them understand why their answer was wrong or how to improve.
✅ How to fix it:
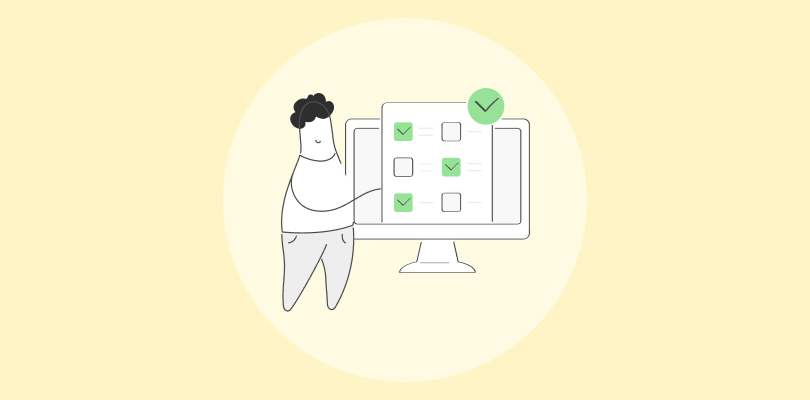
Always include a short explanation after each question so learners know where they went wrong.
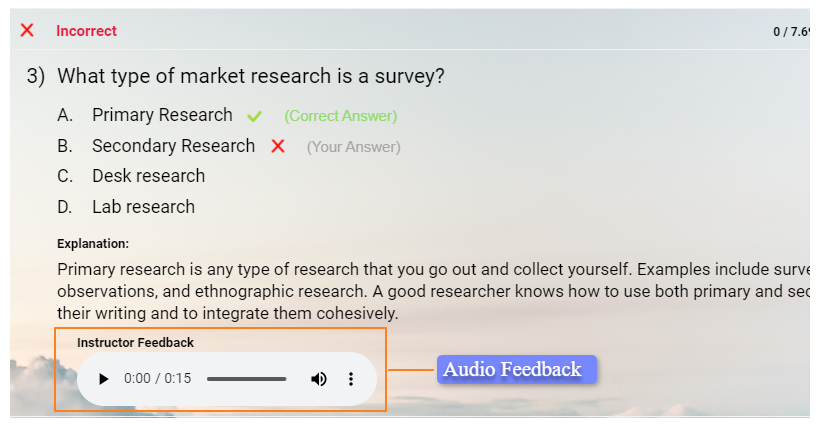
Now, learners can walk away with a better understanding, even if they got the answer wrong.
💡Pro Tip:
If you’re using online test maker software such as ProProfs Quiz Maker, you can make your feedback more useful and engaging by adding an image or linking to a learning resource.
Enhance Learning With Well-Designed Online Quizzes
A well-crafted quiz does more than just test knowledge—it enhances learning, keeps participants engaged, and provides meaningful insights. But common quizzing mistakes, like vague questions or poorly structured answer choices, can make assessments frustrating and ineffective. Fixing these issues ensures that quizzes truly measure understanding and deliver real value.
Another mistake that often goes unnoticed is choosing the wrong quiz maker. Even well-written quizzes can fall short if the platform lacks customization, insightful reporting, or flexible question types.
With ProProfs Quiz Maker, you get everything needed to create clear, engaging, and effective assessments. You can start for free with ProProfs’ forever free plan, which includes essential features like AI-powered quiz generation, 20+ question types, anti-cheating settings, automated grading, reporting, and more—making it easy to create high-quality quizzes effortlessly.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes a quiz successful?
A successful quiz is clear, fair, and effectively measures knowledge. It avoids vague wording, trick questions, and obvious answer choices while keeping learners engaged. A well-structured quiz includes varied question types, balanced difficulty, and immediate feedback to reinforce learning. Choosing the right quiz maker also plays a key role in ensuring a smooth experience.
How to make a quiz more engaging?
To make a quiz engaging, use a mix of question types like multiple-choice, fill-in-the-blank, and scenario-based questions. Keep the wording clear and concise, and avoid repetitive formats. Adding images, videos, or real-world scenarios can make the quiz feel interactive. Also, providing instant feedback helps learners stay motivated and improves retention.
Is a quiz more important than a test?
Quizzes and tests serve different purposes. A quiz is often shorter and designed for quick knowledge checks, reinforcing learning in a low-pressure setting. A test is usually more comprehensive and evaluates a learner’s overall understanding of a topic. While tests measure performance, quizzes help with active recall and ongoing engagement, making them a key part of effective learning.
What is the rule for multiple-choice questions?
A good multiple-choice question should have one clear correct answer and well-balanced distractors. The answer choices should be similar in length and structure to prevent giving away the correct option. When you write multiple-choice questions, avoid using "all of the above" or "none of the above" too frequently, as they can encourage guessing. Ideally, limit options to three to four to keep the question clear and manageable.

 We'd love your feedback!
We'd love your feedback! Thanks for your feedback!
Thanks for your feedback!