What Is Renewable and Nonrenewable Energy Resources? Definition, Examples & Key Concepts
Lesson Overview
Energy powers everything we do, from turning on lights and charging devices, to cooking meals and driving cars. Understanding renewable and nonrenewable energy resources helps us recognize their importance, how they're used, and their impact on our environment. This lesson explores the different types of energy resources clearly and engagingly, highlighting their benefits, limitations, and how they shape our daily lives.

What Are Energy Resources?
Energy resources provide the power needed for our everyday activities, like lighting homes, running cars, and charging electronic devices. Energy comes from different sources, classified into two main types: renewable and nonrenewable. Understanding these helps us make smart decisions for our planet's future.
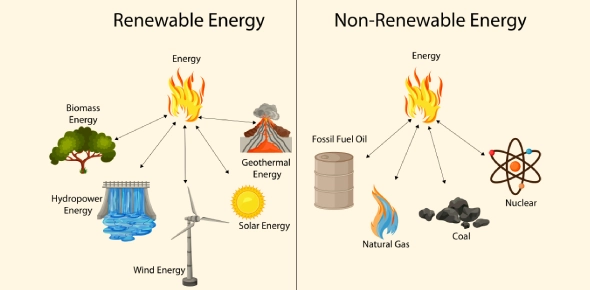
What Are Renewable Energy Resources?
Renewable energy resources are naturally replenished sources of energy that will never run out. They have minimal environmental impacts and help reduce pollution.
Types of Renewable Energy:
1. Solar Energy
Solar energy is energy from the sun, captured using solar panels.
- How it Works: Sunlight is turned into electricity or heat.
- Advantages: Does not produce pollution; abundant and free.
- Disadvantages: Depends on weather and daytime availability.
2. Wind Energy
Wind energy uses wind turbines to convert wind into electricity.
- How it Works: The wind moves turbine blades connected to generators.
- Advantages: Clean energy source; cost-effective.
- Disadvantages: Requires windy locations; turbines can affect wildlife.
3. Hydropower
Hydropower generates electricity from flowing water, typically using dams.
- How it Works: Water flows through dams, spinning turbines.
- Advantages: Reliable and clean; easy to control energy production.
- Disadvantages: Can disrupt natural water flow and wildlife habitats.
4. Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy uses heat from within the Earth.
- How it Works: Heat from beneath the Earth's surface heats water into steam, turning turbines.
- Advantages: Constant and reliable; minimal surface impact.
- Disadvantages: Limited to areas near tectonic plates; high setup costs.
5. Biomass Energy
Biomass energy uses organic material (like plants and animal waste).
- How it Works: Organic matter is burned or converted into biofuels.
- Advantages: Reduces waste; renewable source.
- Disadvantages: Burning biomass can produce air pollution, and may impact the food supply.
Ready to Challenge Yourself? Start the Quiz!
What Are Nonrenewable Energy Resources?
Nonrenewable energy resources exist in limited amounts and cannot be replaced quickly enough to keep pace with usage. They are known for significant environmental impacts.
Types of Nonrenewable Energy:
1. Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels include coal, oil, and natural gas formed from ancient plant and animal remains.
- How it Works: Burned to create heat, generating electricity or powering engines.
- Advantages: Provide large amounts of energy; widely available infrastructure.
- Disadvantages: Causes pollution, contributes to climate change; finite resources.
2. Nuclear Energy
Nuclear energy is generated through the fission of uranium atoms.
- How it Works: Atoms are split, releasing heat used to generate electricity.
- Advantages: Produces significant energy; low air pollution.
- Disadvantages: Produces dangerous radioactive waste; high risks in accidents.
Comparing Renewable and Nonrenewable Energy
| Factor | Renewable Energy | Nonrenewable Energy |
| Availability | Endless supply; constantly replenished | Limited supply; takes millions of years |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal pollution and low emissions | High pollution, contributes to global warming |
| Cost | High initial setup but lower long-term costs | Lower initial setup but higher long-term cost |
| Sustainability | Highly sustainable | Unsustainable |
What Is the Importance of Energy Conservation?
Energy conservation involves reducing energy consumption by using less energy or using it more efficiently.
Why Conserve Energy?
- Protects our environment by reducing pollution.
- Saves money by lowering energy bills.
- Helps extend nonrenewable resource lifespan.
Ways to Conserve Energy:
- Turning off lights and electronics when not in use.
- Using energy-efficient appliances and bulbs.
- Walking, cycling, or using public transportation to reduce fuel use.
Quiz Time! Put Your Knowledge to the Test!
Rate this lesson:
 Back to top
Back to top