Human Respiratory System Lesson: How We Breathe
Lesson Overview
The human respiratory system is responsible for bringing oxygen into the body and removing carbon dioxide, a waste product produced by cells. This system involves a complex network of organs and tissues that work together to ensure that every cell in the body gets the oxygen it needs to function.

In this lesson, we'll explore the parts of the respiratory system, how breathing works, and the importance of keeping our lungs healthy.
The Components of the Respiratory System
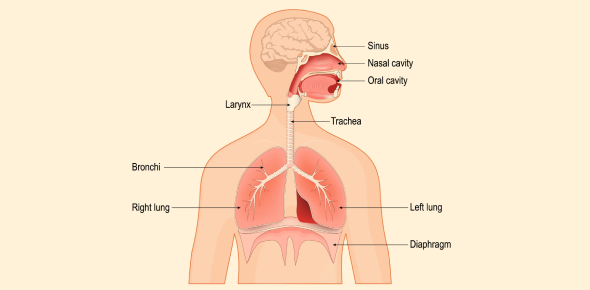
The respiratory system includes several key organs that work together to allow us to breathe. The main components of the system are the nose, trachea, lungs, and diaphragm. Let's take a closer look at each part:
1. Nose and Nasal Cavity
When you breathe in, the air first enters through the nose or mouth. The nose is the primary entry point, and it has tiny hairs and mucus that help filter the air. The nasal cavity also warms and moistens the air, which makes it easier for the lungs to process it. The air then travels down the trachea (windpipe) and into the lungs.
2. Trachea (Windpipe)
The trachea is a tube that carries air from the nose to the lungs. It is lined with tiny hair-like structures called cilia that help trap dust, bacteria, and other harmful particles to keep them from entering the lungs.
3. Lungs
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system. They are responsible for exchanging gases-taking in oxygen from the air and releasing carbon dioxide from the body. The lungs are made up of tiny air sacs called alveoli, where the exchange of gases takes place.
4. Diaphragm
The diaphragm is a large, dome-shaped muscle located at the bottom of the chest. It plays a crucial role in the breathing process. When the diaphragm contracts, it pulls downward, creating space in the chest for the lungs to expand. When the diaphragm relaxes, it pushes upward, helping to push air out of the lungs.
How Breathing Works
Breathing is the process of moving air into and out of the lungs. It involves two main steps: inhalation (breathing in) and exhalation (breathing out). Here's how each step works:
1. Inhalation (Breathing In)
- When you inhale, your diaphragm contracts and moves downward, while your ribcage expands. This creates more space in your chest for your lungs to fill with air.
- The air travels through your nose or mouth, down the trachea, and into the lungs.
- Inside the lungs, the air reaches the alveoli (tiny air sacs). Here, oxygen from the air passes into the blood, and carbon dioxide from the blood moves into the alveoli to be exhaled.
2. Exhalation (Breathing Out)
- When you exhale, your diaphragm relaxes and moves upward, and your ribcage contracts. This reduces the space in your chest and pushes air out of the lungs.
- The air carrying carbon dioxide exits the lungs, travels up the trachea, and leaves the body through the mouth or nose.
This entire process is continuous, happening every time we breathe. It allows our body to get oxygen and remove carbon dioxide.
The Role of Alveoli in Gas Exchange
Alveoli are tiny, balloon-like structures in the lungs where the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place. Each alveolus is surrounded by a network of capillaries, which are tiny blood vessels.
- Oxygen from the air you breathe moves through the thin walls of the alveoli and into the blood in the capillaries.
- Carbon dioxide from the blood moves in the opposite direction, through the alveoli walls, and is exhaled from the body.
This gas exchange is essential for providing oxygen to the body's cells and removing waste products like carbon dioxide.
Diseases of the Respiratory System
The respiratory system can be affected by a number of diseases, some of which can make breathing difficult. Let's look at a few common respiratory diseases:
1. Asthma
Asthma is a chronic condition where the airways in the lungs become inflamed and narrow, making it hard to breathe. This can cause wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath. Asthma can be triggered by allergens, exercise, or cold air.
2. Bronchitis
Bronchitis is the inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which carry air to the lungs. It can be caused by viruses, bacteria, or smoking. Symptoms include coughing, chest discomfort, and difficulty breathing.
3. Emphysema
Emphysema is a progressive disease that causes damage to the alveoli in the lungs. As the alveoli become damaged, it becomes harder for oxygen to enter the blood, leading to difficulty breathing. Emphysema is often caused by long-term exposure to smoking or air pollution.
4. Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an infection in the lungs that causes the alveoli to fill with fluid or pus, making it difficult for oxygen to be absorbed. Symptoms include fever, coughing, and difficulty breathing. Pneumonia can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
The Importance of Healthy Lungs
Taking care of our respiratory system is essential for staying healthy. Here are a few tips for maintaining healthy lungs:
1. Avoid Smoking
Smoking is one of the leading causes of lung disease. It damages the airways, increases mucus production, and can lead to diseases like chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Quitting smoking or never starting is the best way to protect your lungs.
2. Exercise Regularly
Exercise strengthens the lungs and helps improve their capacity. It also helps increase the efficiency of the heart and lungs, ensuring that oxygen is effectively transported to your body.
3. Avoid Polluted Air
Air pollution can irritate the lungs and contribute to respiratory diseases. If you live in an area with poor air quality, try to limit outdoor activities when the pollution level is high.
4. Breathe Clean Air
Using air purifiers at home or in the classroom can help remove dust, allergens, and pollutants from the air, providing a healthier environment for your lungs.
Why is the Respiratory System So Important?
The respiratory system is crucial because it provides the body with the oxygen it needs to survive and removes carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism. Without this system, our cells would not get the oxygen they need for energy production, and the body would not be able to get rid of harmful waste gases.
It also helps in maintaining the body's acid-base balance by controlling the levels of carbon dioxide in the blood.
Fun Facts About Breathing
- You breathe about 20,000 times a day! That's a lot of breaths!
- The average person breathes in about 11,000 liters of air per day.
- Your lungs have about 600 million alveoli, which is a huge surface area for gas exchange.
Rate this lesson:
 Back to top
Back to top
(95).jpg)
