What Is Renewable Energy Types, Advantages, and Global Impact? Definition, Examples & Key Concepts
Lesson Overview
Renewable energy refers to energy derived from natural sources that are continuously replenished, such as sunlight, wind, water, and geothermal heat. Unlike fossil fuels, renewable energy sources do not deplete over time and produce little or no greenhouse gas emissions. This lesson explores the different types of renewable energy, solar, wind, hydro, biomass, and geothermal, their benefits for the environment and economy, and their growing role in addressing climate change and global energy demand. Understanding renewable energy is essential for building a more sustainable, cleaner, and energy-secure future.
What Is Renewable Energy?
Renewable energy is energy that is generated from natural resources that are constantly replenished by environmental processes. Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and emit greenhouse gases when burned, renewable energy sources are sustainable and clean, making them essential for reducing environmental impact and supporting long-term energy needs.
Key Characteristics of Renewable Energy:
- Comes from sources like sunlight, wind, water, biomass, and geothermal heat
- Naturally replenished over short time scales
- Produces little or no carbon emissions
- Can be used for electricity, heating, cooling, and transportation
Main Renewable Energy Sources:
| Source | Description |
|---|---|
| Solar | Captures sunlight using panels to produce electricity |
| Wind | Converts wind movement into electrical energy using turbines |
| Hydropower | Uses flowing water to generate power through turbines |
| Biomass | Produces energy from organic materials like wood and crop waste |
| Geothermal | Harnesses heat from beneath Earth's surface |
What Are the Types of Renewable Energy?
Renewable energy types are based on natural processes that are continuously replenished. These energy sources are sustainable, environmentally friendly, and essential for reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
1. Solar Energy
- Originates from sunlight
- Captured using photovoltaic panels or solar thermal collectors
- Used for generating electricity, heating water, and powering buildings
- Works best in sunny climates and can be stored in batteries
2. Wind Energy
- Generated by wind turbines that convert wind movement into electricity
- Onshore and offshore wind farms harness kinetic energy from air
- Clean, efficient, and increasingly cost-effective
- Output depends on wind speed and location
3. Hydropower (Water Energy)
- Uses flowing or falling water to turn turbines and produce electricity
- Found in dams, rivers, or pumped storage systems
- Provides steady, large-scale power but may impact aquatic habitats
4. Biomass Energy
- Comes from organic materials like plants, wood, crop waste, and animal manure
- Can be burned directly or converted into biofuels (ethanol, biodiesel)
- Generates heat, electricity, or fuel
- Considered renewable if harvested sustainably
5. Geothermal Energy
- Extracted from heat within the Earth's crust
- Used for electricity generation and direct heating applications
- Reliable and low in emissions
- Best suited for geologically active areas
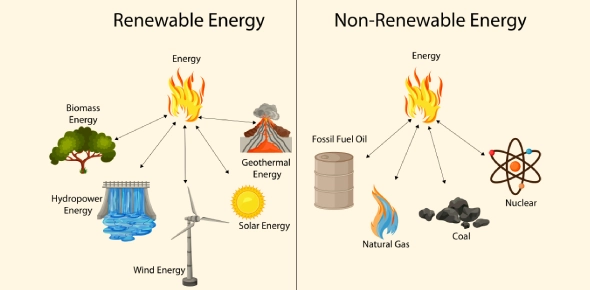
What Are Renewable and Non-Renewable Energy Resources?
Energy resources are classified into two main categories based on their availability and rate of replenishment: renewable and non-renewable. Understanding the difference between them is essential for making informed decisions about energy use, sustainability, and environmental impact.
Renewable Energy Resources
Renewable energy resources are naturally replenished on a human timescale. They are clean, sustainable, and abundant, making them key to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and environmental degradation.
Common Renewable Resources:
| Resource | Source | Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Solar Energy | Sunlight | Electricity, heating |
| Wind Energy | Moving air | Electricity |
| Hydropower | Flowing water | Electricity |
| Biomass | Organic matter | Heat, fuel, electricity |
| Geothermal | Earth's internal heat | Electricity, space heating |
Advantages:
- Replenished naturally
- Low environmental impact
- Reduces air pollution and carbon emissions
Non-Renewable Energy Resources
Non-renewable energy resources come from finite sources that take millions of years to form. Once used, they cannot be replaced within a short period. Their extraction and use cause pollution and contribute significantly to climate change.
Common Non-Renewable Resources:
| Resource | Source | Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Coal | Fossilized plant material | Electricity generation |
| Oil (Petroleum) | Ancient marine organisms | Transportation, fuel |
| Natural Gas | Decomposed organic matter | Heating, electricity, industry |
| Nuclear Fuel | Uranium or thorium | Electricity via nuclear reactions |
Disadvantages:
- Limited supply
- Produces greenhouse gases and waste
- High environmental and health risks
Comparison Table
| Feature | Renewable Resources | Non-Renewable Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Availability | Unlimited, naturally replenished | Finite, exhaustible |
| Environmental Impact | Low | High |
| Sustainability | Long-term | Short-term |
| Energy Examples | Solar, wind, hydro | Coal, oil, natural gas, uranium |
| Emissions | Minimal or none | High CO2 and pollutant output |
Take This Quiz
How Can Renewable Energy Benefit the Environment?
Renewable energy benefits the environment by reducing pollution, conserving natural resources, and supporting ecosystem health. Unlike fossil fuels, renewable sources such as sunlight, wind, water, and biomass produce little or no harmful emissions, making them essential for protecting the planet.
Key Environmental Benefits of Renewable Energy:
1. Reduces Air Pollution
- Renewable sources like solar and wind generate electricity without burning fuel
- This avoids the release of harmful pollutants such as carbon dioxide CO2, sulfur dioxide SO2, and nitrogen oxides NOx
- Helps improve air quality, especially in urban and industrial areas
2. Lowers Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- Replacing fossil fuels with renewable energy reduces CO2 emissions, the main driver of climate change
- Helps slow global warming and reduce the frequency of extreme weather events
3. Conserves Water Resources
- Many renewable technologies (solar, wind) use little or no water to operate
- This reduces pressure on freshwater supplies, especially important in arid regions
4. Reduces Habitat and Land Degradation
- Properly planned renewable projects can avoid large-scale land destruction
- Unlike mining and drilling, renewables preserve soil, forests, and habitats
- Offshore wind farms and rooftop solar have low land impact
5. Minimizes Environmental Accidents
- Renewable systems are less prone to catastrophic events such as oil spills, gas leaks, or nuclear accidents
- Safer for nearby communities and ecosystems
6. Promotes Sustainable Development
- Encourages cleaner production methods and sustainable land use
- Supports green jobs and reduces dependence on extractive industries
Conclusion
In this lesson on renewable energy, we delved into its critical importance in the global transition toward sustainability. We learned about the various forms of renewable energy-solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal, and biomass-and how they harness natural processes to produce clean, sustainable power. These energy sources are not only vital in reducing dependence on fossil fuels but also offer significant environmental, economic, and social benefits, such as lowering greenhouse gas emissions, improving public health, and driving job creation in the green energy sector.
Take This Quiz
Rate this lesson:
 Back to top
Back to top