Division – Definition, Rules, Properties & Examples: A Complete Guide with Real-World Relevance
Lesson Overview
Sharing equally is important. Division helps do this with numbers. If you have 12 candies and 3 candies, the division tells you each friend gets 4 candies. Division splits big numbers into smaller, equal groups.
Think of division as the opposite of multiplication. While multiplication combines groups, division separates them. Just like subtraction is the opposite of addition.
What Is Division?
Division is the process of splitting a number into equal parts. It helps to find out how many times one number fits into another.
For example:
- If 12 apples are divided equally into 3 baskets, each basket will have 4 apples.
- If 20 pencils are grouped into sets of 5, there will be 4 groups.
Division can be represented using the division symbol (÷) or a fraction bar (/).
Take This Quiz -
Basic Rules Of Division
Division involves a series of steps to break down the problem. These steps help in finding the correct result efficiently.
Step 1: Identify the dividend and divisor, and place them in their proper positions.
Step 2: Multiply the divisor by a suitable number to get as close as possible to the dividend.
Step 3: Subtract the product from the dividend to find the difference.
Step 4: Bring down the next number and repeat steps 2 and 3 until the remainder is smaller than the divisor.
Take This Quiz -
Properties of Division
Division has some special rules, just like a game! These rules help us understand how numbers behave when we divide them.
| Property | Description | Example |
| Division by 1 | When dividing any number by 1, the answer is the number itself. | 9 ÷ 1 = 9 |
| Division by itself | When dividing any number (except 0) by itself, the answer is always 1. | 5 ÷ 5 = 1 |
| Division by 0 | Dividing any number by 0 is undefined – it's like trying to share something with no one! | 10 ÷ 0 = undefined |
| Zero divided by a number | When 0 is divided by any number (except 0), the answer is always 0. | 0 ÷ 8 = 0 |
Take This Quiz -
Solving Division Problems Step-By-Step
Long division is a method for dividing large numbers into smaller groups. It simplifies complex division problems by breaking them down into a series of manageable steps.
Long Division Steps
Every long division can be solved with the five steps given below.
Here's an example to understand the division steps.
Take This Quiz-
Solved Examples On Division
Example 1: 12 ÷ 3 (Simple Division)
Solution: 12 ÷ 3 = 4
Quotient: 4, Remainder: 0
Example 2: 18 ÷ 6 (Simple Division)
Solution: 18 ÷ 6 = 3
Quotient: 3, Remainder: 0
Example 3: 35 ÷ 6 (With Remainder)
Solution: 35 ÷ 6 = 5 R 5
Quotient: 5, Remainder: 5
Example 4: 144 ÷ 12 (Long Division)
Solution: 144 ÷ 12 = 12
Quotient: 12, Remainder: 0
Example 5: 50 ÷ 7 (With Remainder)
Solution: 50 ÷ 7 = 7 R 1
Quotient: 7, Remainder: 1
Take This Quiz -
Rate this lesson:
 Back to top
Back to top
(351).webp)
(358).webp)
(267).jpg)
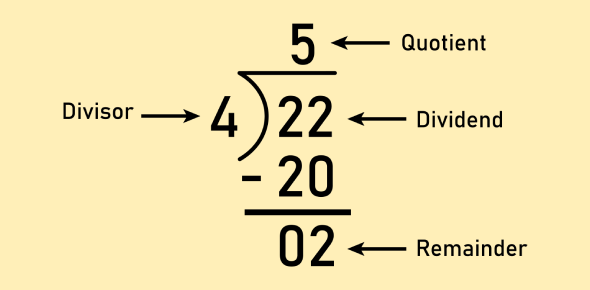
(19).webp)