How Plants Live and Grow: Life Cycles, Reproductive Strategies, and Structures
Lesson Overview
Plants are one of the most important life forms on Earth. They are essential for life to exist, as they provide food, oxygen, shelter, and many raw materials. But how do plants live and grow? What do they need from their environment? How are they able to develop from a small seed into a full-grown plant? This lesson explores the major components, structures, and processes that contribute to plant survival and growth.

Essential Needs for Plant Life
For a plant to live and grow properly, it must receive several vital resources from its surroundings. Each of these resources supports a different function in the plant's life.
Water
Water is essential for every plant. It is absorbed by the roots from the soil and transported through the stem to all parts of the plant. Water not only helps dissolve minerals and nutrients in the soil, but it is also a raw material used in photosynthesis, the process by which plants make their own food.
Sunlight
Sunlight provides energy for the plant to produce food. In the leaves, a substance called chlorophyll captures energy from the sun and uses it to turn water and carbon dioxide into glucose (sugar), a type of food.
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a gas present in the air. Plants absorb it through tiny pores on the undersides of their leaves called stomata. It combines with water and sunlight to create food through photosynthesis.
Minerals and Nutrients
Minerals are natural, nonliving materials found in soil. They are absorbed by plant roots and are necessary for healthy growth and development. Important minerals include nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and calcium. These minerals support functions like flower and fruit production, stem strength, and leaf development.
Take This Quiz -
Plant Structures and Their Functions
Each part of a plant is structured in a way that supports the overall growth, health, and reproduction of the plant. Understanding the major parts helps explain how plants manage to grow, absorb nutrients, and make new plants.
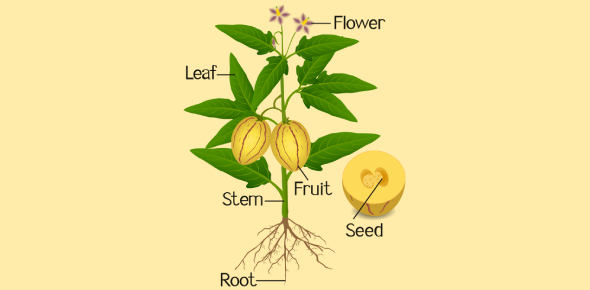
Roots
Roots anchor the plant firmly in the ground and absorb water and nutrients from the soil. Fine root hairs increase the surface area to absorb more efficiently. In some plants, roots also serve as storage organs, holding extra food for later use.
Stems
Stems support the plant and act as transportation highways. Inside the stem are tubes called xylem and phloem. Xylem moves water and minerals upward from the roots to the leaves, while phloem carries sugars made in the leaves to other parts of the plant. Without a healthy stem, the plant cannot distribute food or water effectively.
Leaves
Leaves are the food factories of the plant. Through photosynthesis, leaves use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose. Oxygen, a by-product of this process, is released back into the air. The stomata on leaves also allow the exchange of gases-taking in carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen.
The Life Cycle of a Plant
A plant's life is not a single event; it is a continuous process that includes growth, reproduction, and eventually death. The entire process is known as the life cycle.
Seed
All plants begin as seeds. Inside the seed is a tiny plant embryo and stored food. The food storage part is called the seed leaf or cotyledon, and it provides nourishment for the plant until it can start making its own food.
Germination
When a seed is placed in the right environment-usually with warmth, moisture, and air-it begins to sprout. This first stage of growth is called germination. The root comes out first to anchor the plant, followed by the shoot that grows upward.
Growth
Once the seedling forms leaves, it starts to produce its own food through photosynthesis. It grows larger and forms more complex structures like branches and flowers.
Reproduction
Most plants reproduce using flowers. Inside the flower are male and female parts. The anther produces pollen, a powdery substance that contains the male reproductive cells. The stigma receives the pollen during a process called pollination.
Take This Quiz -
Pollination and Seed Formation
Pollination is an important step in plant reproduction. It happens when pollen from the male part of the flower reaches the female part. This can occur in various ways, including through the wind, insects, and animals.
One of the most effective pollinators is the bee. Bees visit flowers to collect nectar. While doing so, pollen sticks to their bodies and is transferred from one flower to another. This process allows the flower to produce seeds.
Once the pollen reaches the ovule in the flower, fertilization takes place. A seed is formed, which can then grow into a new plant, continuing the life cycle.
Flower Parts and Their Roles
Flowers are the reproductive structures of many plants. They are not only beautiful but also essential to plant reproduction. One of the most visible parts is the petal.
Petals
Petals are often brightly colored and fragrant. Their main function is to attract pollinators, especially bees and butterflies. The color, shape, and scent guide insects to the pollen, helping with the transfer needed for fertilization.
Take This Quiz -
Evergreens and Conifers
Not all plants lose their leaves in the winter. Evergreen trees, such as pine trees, keep their leaves year-round. These trees are also conifers, which means they produce cones instead of flowers. Their leaves are usually needle-shaped and help them conserve water in cold or dry climates.
This is different from deciduous trees, which shed their leaves in the fall. Conifers are well-adapted to survive in regions with harsh weather conditions.
Understanding how plants live and grow is fundamental to appreciating the natural world around us. Plants rely on several key ingredients from their environment-sunlight, water, minerals, and carbon dioxide-to grow and survive. Each part of the plant has a specific role: roots absorb water and nutrients, stems transport essential materials, leaves create food, and flowers ensure reproduction through pollination and seed formation.
Take This Quiz -
Rate this lesson:
 Back to top
Back to top